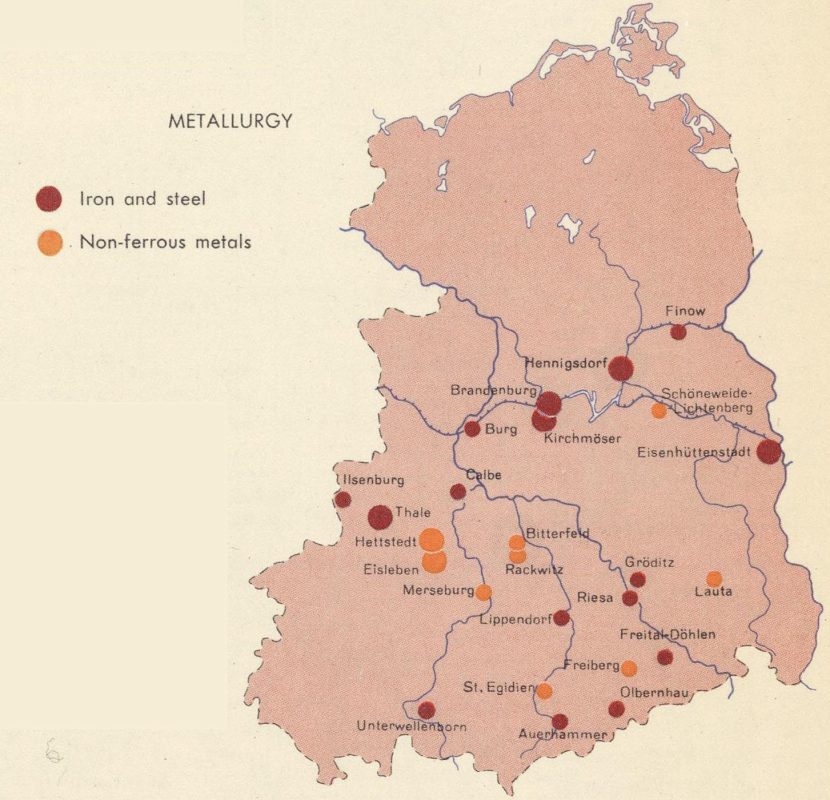
“Experience the Strength of German Steel: Germany 2020 Steel Consumption”
Germany is one of the world’s leading steel consumers, with an estimated consumption of around 43 million metric tons in 2020. This is a significant increase from the 38 million metric tons consumed in 2019. Germany is the largest steel consumer in the European Union and the fourth-largest steel consumer in the world. The country’s steel consumption is driven by its strong manufacturing sector, which is the largest in Europe. Germany is also a major exporter of steel, with exports accounting for around 20% of its total steel production. In this article, we will take a closer look at Germany’s steel consumption in 2020 and the factors driving it.
Germany is one of the world’s leading steel consumers, and its steel consumption has a significant impact on the global economy. In this article, we’ll take a look at the economic implications of Germany’s steel consumption and how it affects the global market.
First, let’s consider the direct economic impact of Germany’s steel consumption. Germany is the world’s fourth-largest steel consumer, and its steel consumption accounts for around 8% of the global total. This means that Germany’s steel consumption has a direct impact on the global steel market, as it affects the supply and demand of steel.
The indirect economic impact of Germany’s steel consumption is also significant. Germany is a major producer of steel-related products, such as automobiles, machinery, and construction materials. As such, its steel consumption affects the production of these products, which in turn affects the global economy.
Furthermore, Germany’s steel consumption has an impact on the global price of steel. As Germany is a major consumer of steel, its demand for steel affects the global price of steel. This, in turn, affects the cost of production for other countries that rely on steel for their own production.
Finally, Germany’s steel consumption has an impact on the global environment. Steel production is a major source of air pollution, and Germany’s steel consumption contributes to this pollution. This has a negative effect on the environment, as well as on the health of people living in areas affected by steel production.
In conclusion, Germany’s steel consumption has a significant impact on the global economy and environment. Its direct and indirect economic impacts affect the global steel market, the production of steel-related products, and the global price of steel. Additionally, its steel consumption contributes to air pollution, which has a negative effect on the environment and people’s health.
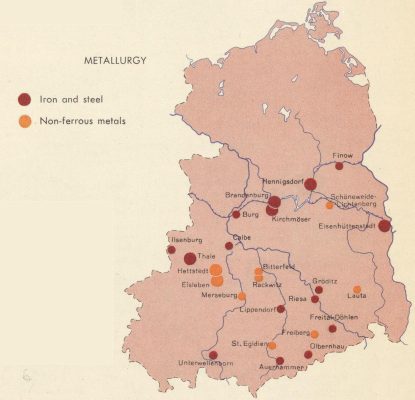
Germany is a major player in the global automotive industry, and its steel consumption plays a significant role in the production of cars. In this analysis, we’ll take a closer look at how Germany’s steel consumption affects the automotive industry, and what implications this has for the future of the industry.
First, it’s important to understand the scale of Germany’s steel consumption. According to the World Steel Association, Germany is the world’s fourth-largest steel consumer, behind China, the United States, and Japan. In 2018, Germany consumed around 37 million metric tons of steel, with the majority of this being used in the automotive industry. This is a significant amount of steel, and it’s clear that Germany’s steel consumption has a major impact on the automotive industry.
So, what does this mean for the automotive industry? Well, it means that Germany’s steel consumption has a direct effect on the production of cars. The more steel that is consumed, the more cars that can be produced. This is especially true for luxury cars, which require more steel than other types of vehicles. As such, Germany’s steel consumption has a direct impact on the production of luxury cars, and this has implications for the future of the industry.
Furthermore, Germany’s steel consumption also affects the cost of cars. As more steel is consumed, the cost of production increases. This means that cars produced in Germany are likely to be more expensive than those produced elsewhere. This could have a significant impact on the global automotive industry, as it could make German cars less competitive in the global market.
Finally, Germany’s steel consumption also affects the environment. Steel production is a major source of pollution, and the more steel that is consumed, the more pollution is created. This could have a negative impact on the environment, and it’s something that needs to be taken into consideration when looking at the future of the automotive industry.
In conclusion, Germany’s steel consumption plays a major role in the automotive industry. It affects the production of cars, the cost of cars, and the environment. As such, it’s important to consider the implications of Germany’s steel consumption when looking at the future of the automotive industry.

Germany is one of the world’s largest steel consumers, and its steel consumption has a significant impact on the global market. In recent years, Germany’s steel consumption has been on the rise, and this has had a ripple effect on the global steel market.
To begin with, Germany’s increased steel consumption has caused a surge in global steel prices. As Germany’s demand for steel has grown, so too has the price of steel on the global market. This has had a direct impact on other countries that rely on steel imports, as they have had to pay more for the same amount of steel.
Furthermore, Germany’s increased steel consumption has caused a shortage of steel in other countries. As Germany has been buying up more steel, other countries have had to compete for the remaining supply. This has caused a shortage of steel in some countries, which has had a negative impact on their economies.
Finally, Germany’s increased steel consumption has caused a shift in the global steel market. As Germany has become a major player in the steel market, other countries have had to adjust their strategies in order to remain competitive. This has caused a shift in the global steel market, as countries have had to focus more on producing higher quality steel in order to remain competitive.
Overall, Germany’s increased steel consumption has had a significant impact on the global market. It has caused a surge in global steel prices, a shortage of steel in other countries, and a shift in the global steel market. As Germany continues to consume more steel, these effects are likely to continue.